
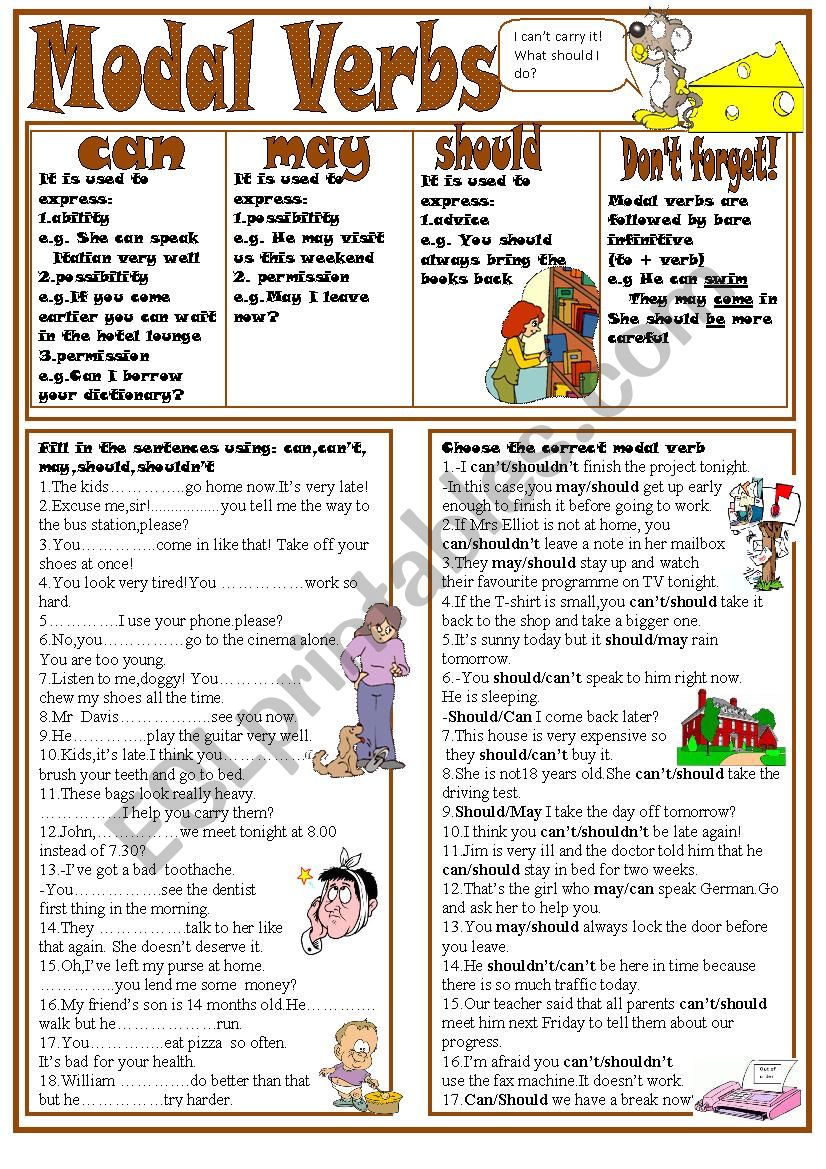
Note that modal verbs are very commonly used in a wide variety of senses-this table doesn’t cover every possible usage. Modal verb tableīelow is a table that illustrates some of the various uses of modal verbs.
Lina must order tickets in advance if she wants to go to the theater.

You may have as many cookies as you’d like. Examples: How to use modal verbsI might walk to work today. Modal verbs come before main verbs and never change form. In sentences containing modal verbs, the main verb typically takes the infinitive form. Max’s father couldn’t work in the garage alone.Modal verbs are used along with a main verb to indicate ability, necessity, possibility, and permission. Was Max able to change the tyre yesterday? Max’s father could remember changing his first tyre. Example: Max’s father could do everything in the garage. The negative couldn’t can be used in all three cases. We use was/were able to when we talk about something specific in the past. We use could for general ability and with the verbs feel, hear, see, smell, taste, remember and understand. * We use could and was/were able for the past of can. Of course, we can also use the alternative forms (except for could) in other tenses. Max’s father also was supposed to/was expected to/was to work in the garage often. Max should work in the garage more often. To be supposed to/to be expected to/to be to Max’s father did not have to worry about his future either. Max’s father was allowed to help at the age of 13. Max can help in the garage at the age of 12. His father was not able to/couldn’t change tyres. His father was not allowed to touch anything dangerous. We use will (not)/shall (not) when we make a predicition about the future, or when we are sure about something in the future.Įxample: The car won’t/shan’t be ready tomorrow.To speculate about something in the past we use can’t/must + have + past participle.Įxample: Max’s father must have worked very hard.


( but not: Max’s grandfather can be retired.)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
